Turbochargers - The Facts
Table of ContentsHow Turbochargers can Save You Time, Stress, and Money.The Only Guide to Turbochargers7 Simple Techniques For Turbochargers
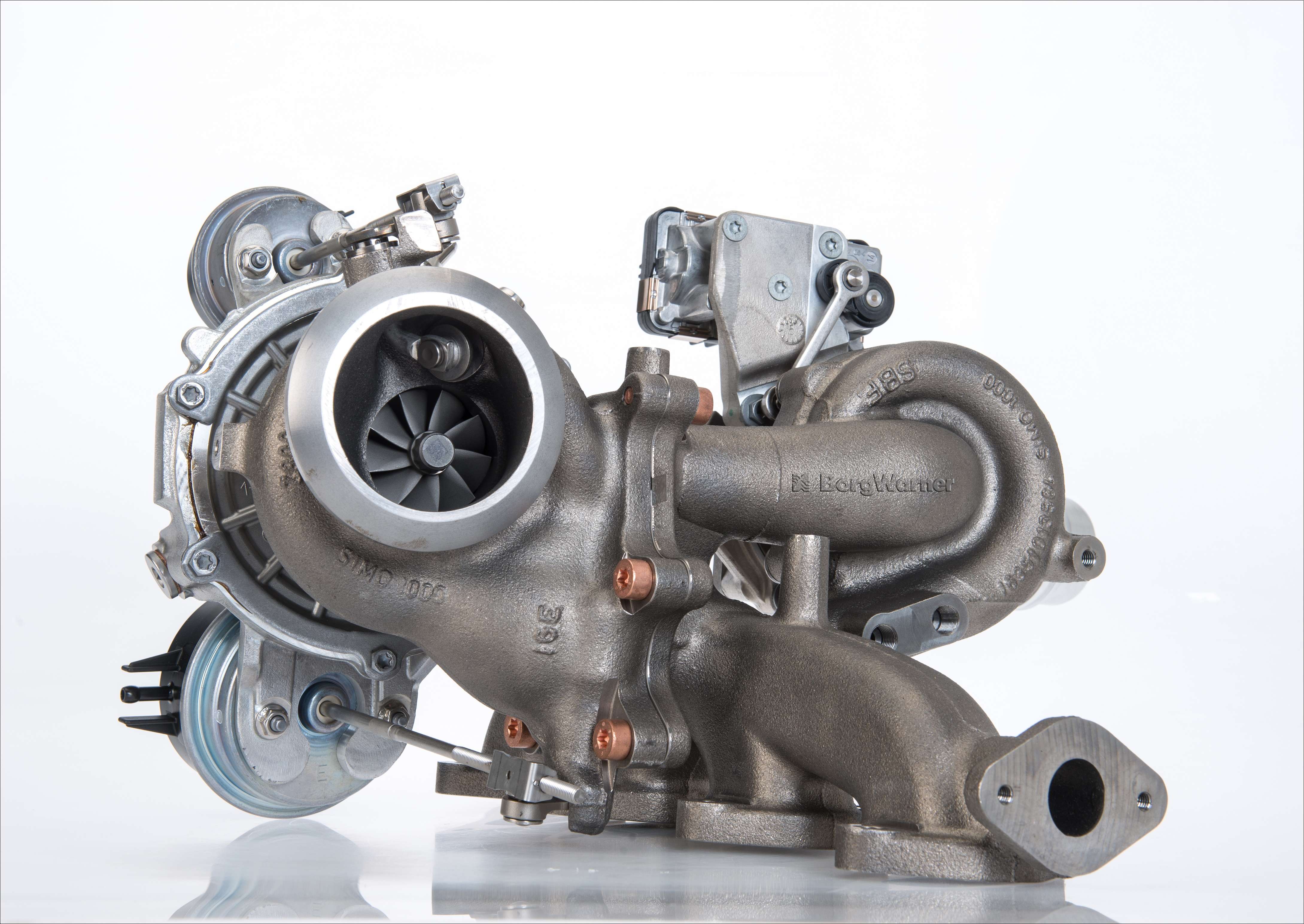
For example, in Opel bi-turbo Diesel, just the smaller sized turbocharger operates at low speed, supplying high torque at 1,5001,700 rpm - turbochargers. Both turbochargers operate together in mid variety, with the smaller one pre-compressing the air, which the bigger one more compresses. A bypass valve controls the exhaust flow to each turbocharger.
Smaller turbochargers have less turbo lag than larger ones, so typically 2 small turbochargers are utilized rather of one big one. This setup is popular in engines over 2. 5-litres and in V-shape or boxer engines. Twin-scroll or divided turbochargers have two exhaust gas inlets and two nozzles, a smaller sharper angled one for quick response and a larger less angled one for peak efficiency.
In twin-scroll styles, the exhaust manifold physically separates the channels for cylinders that can disrupt each other, so that the pulsating exhaust gasses circulation through different spirals (scrolls). With typical shooting order 1342, 2 scrolls of unequal length set cylinders 1 and 4, and 3 and 2. This lets the engine efficiently utilize exhaust scavenging methods, which decreases exhaust gas temperature levels and emissions, enhances turbine performance, and decreases turbo lag obvious at low engine speeds.
The vanes are placed just in front of the turbine like a set of slightly overlapping walls. Their angle is adjusted by an actuator to block or increase air flow to the turbine. This variability maintains a comparable exhaust velocity and back pressure throughout the engine's rev range. The outcome is that the turbocharger improves fuel efficiency without a noticeable level of turbocharger lag.
The compressor is made up of an impeller, a diffuser and a volute real estate. The operating variety of a compressor is explained by the "compressor map". The circulation range of a turbocharger compressor can be increased by permitting air to bleed from a ring of holes or a circular groove around the compressor at a point somewhat downstream of the compressor inlet (however far nearer to the inlet than to the outlet).
Some Known Questions About Turbochargers.
It attains this by forcing a simulation of impeller stall to occur constantly. Enabling some air to leave at this location prevents the beginning of rise and expands the operating range. While peak performances may decrease, high efficiency might be achieved over a higher variety of engine speeds. Increases in compressor efficiency result in somewhat cooler (more thick) intake air, which improves power.
The capability of the compressor to provide high increase at low rpm might also be increased partially (because near choke conditions the compressor draws air inward through the bleed path). Ported shrouds are utilized by lots of turbocharger manufacturers. The centre hub rotating assembly (CHRA) houses the shaft that connects the compressor impeller and turbine.

Ball bearings created to support high speeds and temperature levels are sometimes used rather of fluid bearings to support the turbine shaft. This assists the turbocharger speed up more quickly and lowers turbo lag. Some variable nozzle turbochargers utilize a rotary electric actuator, which uses a direct stepper motor to open and close the vanes, instead of pneumatic controllers that run based on air pressure.
When the pressure of the engine's intake air is increased, its temperature level also increases. This event can be discussed through Gay-Lussac's law, specifying that the pressure of an offered quantity of gas held at constant volume is straight proportional to the Kelvin temperature level. With more pressure being contributed to the engine through the turbocharger, overall temperature levels of the engine will also increase.
The warmer the intake air, the less dense, and the less oxygen available for the combustion event, which reduces volumetric efficiency. Not just does extreme intake-air temperature level minimize effectiveness, it likewise leads to engine knock, or detonation, which is destructive to engines. To compensate for the boost in temperature level, turbocharger units often make use of an intercooler in between succeeding stages of increase to cool off the consumption air.
Facts About Turbochargers Uncovered
There are 2 areas on which intercoolers are important source commonly installed. turbochargers. It can be either installed on top, parallel to the engine, or installed near the lower front of the car. Top-mount intercoolers setups will result in a decrease in turbo lag, due in part by the area of the intercooler being much closer to the turbocharger outlet and throttle body.
Front-mount intercoolers can have the prospective to offer better cooling compared to that of a top-mount. The area in which a top-mounted intercooler is situated, the original source is near among the hottest areas of a cars and truck, right above the engine. This is why most makers consist of large hood scoops to assist feed air to the intercooler while the car is moving, but while idle, the hood scoop supplies little to no advantage.
With more distance to take a trip, the air flowed through a front-mount intercooler might have more time to cool. Methanol/water injection has been around considering that the 1920s however was not made use of till World War II. Adding the mix to consumption of the turbocharged engines reduced operating temperature levels and increased horse power.